Footing Design: Raft or Isolated?
Footing design: Raft or isolated?
This
project is a comparison between the 2 most commonly used types of foundation:
Raft (or mat) and isolated (or spread) footing.
You will find out the differences between these 2 types to know how to choose the correct type for a building (Figures 1 and 2).
Figure 2: Raft foundation.
The
foundation is the structural element that connects a building or any structure to
the ground (Fig. 3).
Figure 3: Foundation of a building.
There
are different types of foundations that you can use for a structure as you can
see in figure 4, but each one has special uses, and you have to know how to
choose the correct foundation type for your structure.
Figure 4: Types of foundation from ACI 318-19 code.
Table 1: How to decide which footing type is better.
|
|
Isolated footing |
Raft footing |
|
Soil bearing capacity |
Use isolated footing if you have a very good soil bearing
capacity > 100 Kpa. |
Low soil bearing capacity. |
|
Area of isolated footing |
Use isolated footing if their area is < 0.5 * area of the
building. |
> 0.5 * area of the building. |
|
Building height |
Building height < 20 m (7 floors as maximum). |
Used in moderate height buildings not very height. |
Advantages of Isolated Footing:
1.
Economical
when columns are placed at longer distances.
2.
Workmen
with little or no knowledge can easily construct.
3. Ease of Constructability: Excavation, Form-work, Reinforcement placement, and placing of Concrete are at ease.
Advantages
of Raft Foundation:
1.
Mat
footing can be provided where the shallow foundation is necessary and when the
soil is poor.
2. Mat foundation requires less earth excavation.
Table 2: Differences in the design between raft foundation and
isolated foundation:
|
|
Isolated footing |
Raft footing |
|
Tension |
@ Bottom |
@ Top |
|
Compression |
@ Top |
@ Bottom |
|
Main bars |
@ Bottom |
@ Top |
Figure 5: Design of isolated and raft foundation.
Differences in the design between isolated and raft foundations:
Ø Isolated foundation left and right parts are like a cantilever
beam, that is exposed to soil load from the bottom.
This cantilever will move to the top, and you will have
tension at the bottom and compression at the top (Fig.5).
And as you know that concrete is weak in tension and
strong in compression, the main reinforcement in an isolated footing will be at
the bottom.
You can add minimum reinforcement at the top.
Ø Raft foundation is like a continuous beam exposed to uniform
soil load at the bottom, and the load from the columns is like the supports of
the beam (like an inverted beam).
As a result, you will have at all the mid spans:
tension at top and compression at bottom, so the main reinforcement in a raft
foundation will be at the top.
But at support, you will have tension at the bottom, so the
main reinforcement will be at the bottom.
And by practice, at the site, the same top and bottom reinforcements
are used in the raft foundation (Fig 9).
Additional reinforcements are always added to the columns (Fig.8).
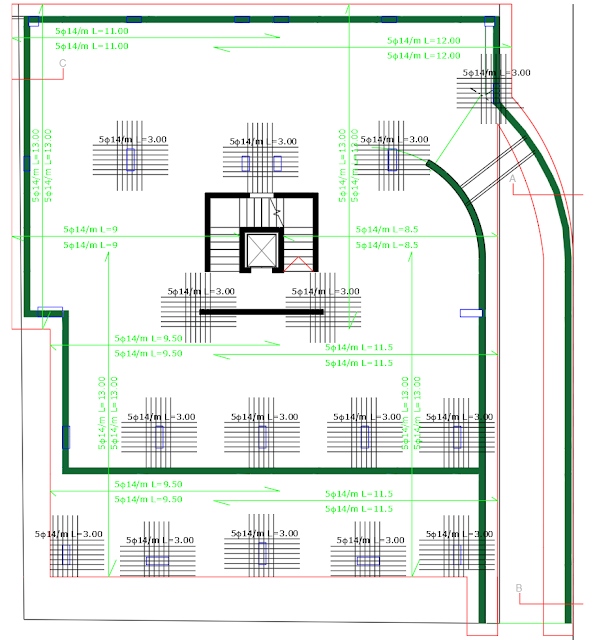
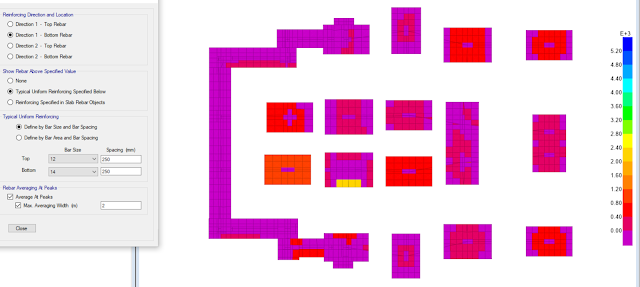
Figure 6: Raft foundation drawing using SAFE software.
Figure 8: Raft foundation AUTOCAD plan.
·
The raft foundation area in
figure 8 is the red perimeter, where we have uniform reinforcements of 5T14 /m
for top and bottom reinforcements in the 2 directions.
Additional reinforcement is added to the
columns.
Figure 9: Raft foundation AUTOCAD section.
Figure 10: Raft foundation reinforcements.
Figure 11: Raft foundation casting.
Figure 12: Isolated footings (connected by tie beams to prevent differential settlement), drawing is on SAFE software.
Figure 17: Isolated footing reinforcement with top reinforcement.
Figure 19: Isolated footing drawing on Revit software.
Conclusion:
The foundation is the first structural element built in any structure, there are also different types of foundation that a civil engineer should know how to design and when to use them.

















Comments
Post a Comment